Before you get lost in the various options and filters, read the previous articles in this series to see what you can achieve with Automations:
- Translate Content Immediately After Uploading with MT
- Fine-Tune Your UX Copy Before Translating It
- Prevent Translation of Unwanted Strings
🧰 Why use filters? 🔗
Filters in our Automations are a powerful way to apply the rules to a subset of keys only.
For example, with an e-commerce app, it is expected to only translate descriptions and longer texts using machine translation and invest extra effort to get product names translated carefully for the target market.
Not all filters are available for all actions, and there are also differences in how filters are used based on the event that triggered the automation run.
♾️ Applying automations to all events 🔗
By default, the automation will run on all events if you don't specify any filters. However, there are still some internal rules applied as well. For example, the Use machine translations action is always run only on the source translations as it doesn't make much sense to use this action in any other way.
❓ How do "include" and "exclude" work? 🔗
Most filters described below allow you to define a list of "include" conditions (or filters) as well as a list of "exclude" conditions.
- If no "include" filters are set, all items will be processed by the automation action unless they match one of the "exclude" filters.
- If the item matches any of the "include" filters, it will be processed by the automation action unless it also matches one of the "exclude" filters.
- The "exclude" filter has a higher priority, meaning that if the item is included and excluded simultaneously, it is not processed by the automation action.
For example, imagine you want to process only keys starting with the prefixa_, so you set up a filter to include only such strings. But some of these strings contain a suffix-zand you do not want these to be processed. By defining both filters, you ensure that only strings that start with the prefixa_and do not end with the suffix-zwill be processed.
➡️ Types of automation filters 🔗
🚩 Filter by Language 🔗
With this filter active, the given automation action is run only if the translations in the selected language/languages initiate the given trigger event.
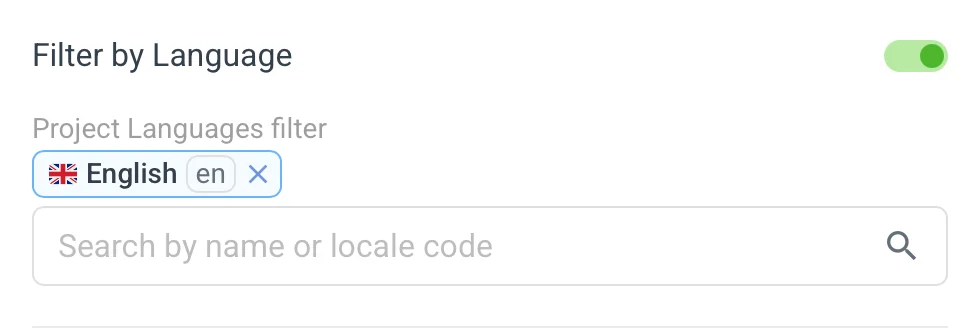
This filtering is available for all actions except the Use machine translations action.
For Copy translations to another language, it only allows you to define a single language, as it wouldn't make sense to copy multiple languages into a single target. You can see this in other actions. Some actions allow you to filter via multiple languages, while others let you select only one.
👥 Filter by User triggering the event 🔗
These are available to all trigger events. With this filter active, the given automation action is run only if the allowed users initiate the given trigger event.
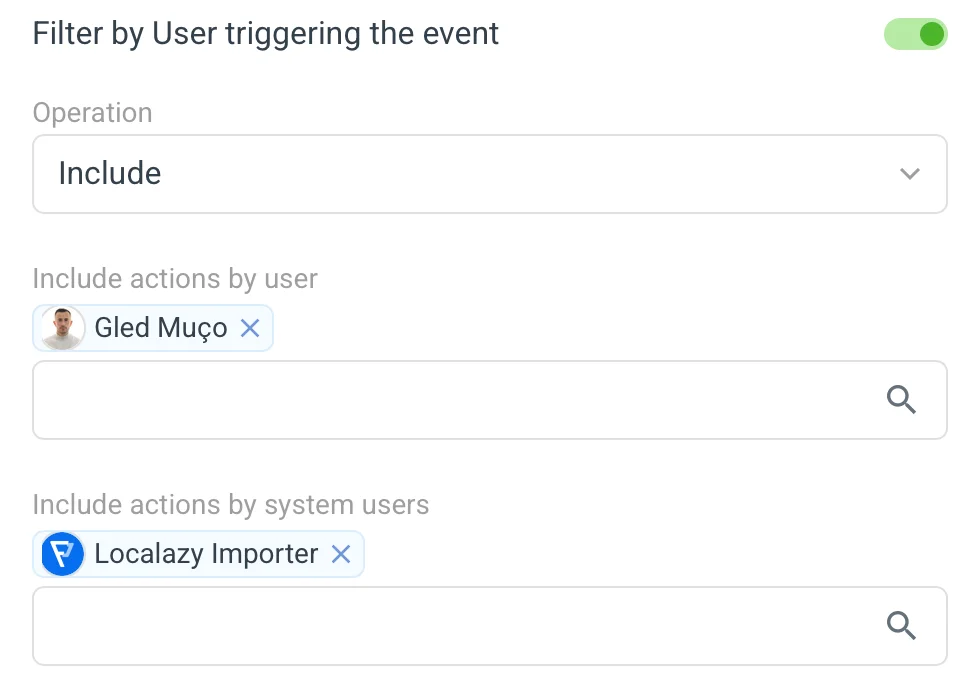
The user depends on the trigger event:
Key or translation uploaded | The user who started the import process |
Key or translation updated | The user who started the import process |
Key or translation deprecated | The user who started the import process |
Key created manually | The user who created the key |
Key translated | The user who translated the key |
Translation reviewed | The user who reviewed the translation |
Manual trigger | The user who triggered the automation run |
Then, we also have the system users, which are names for the actions performed by the platform itself. These are:
- Localazy Importer → Whatever you import into Localazy. For instance, the translations imported when you started the project.
- Localazy InTM → Translation created by using Localazy Translation Memory.
- Machine Translation → Translation created by using machine translation.
- Localazy translation service → Translation created by Localazy’s Continuous Localization Team.
🗣️ Filter by User Role 🔗
This filtering is available for all actions except for Use machine translations.
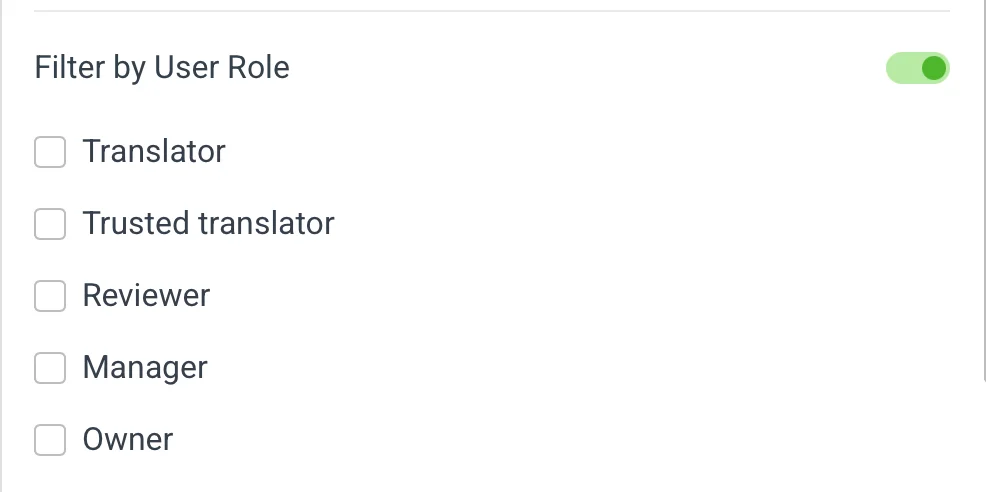
The filter is based on the user role, which is the same user as in User-based filtering, with the selected list. You can choose from a Translator, Trusted Translator, Reviewer, Manager, or Owner.
📌 Filter by the Translation State 🔗
This filtering is available for all actions except for Use machine translations.
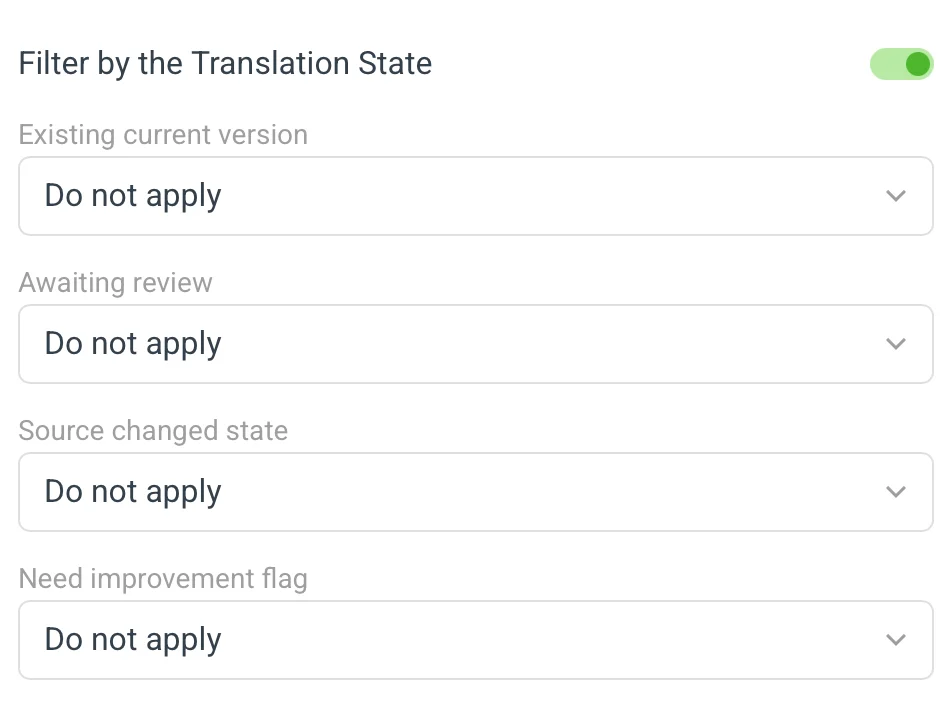
Each filter has three options like this:
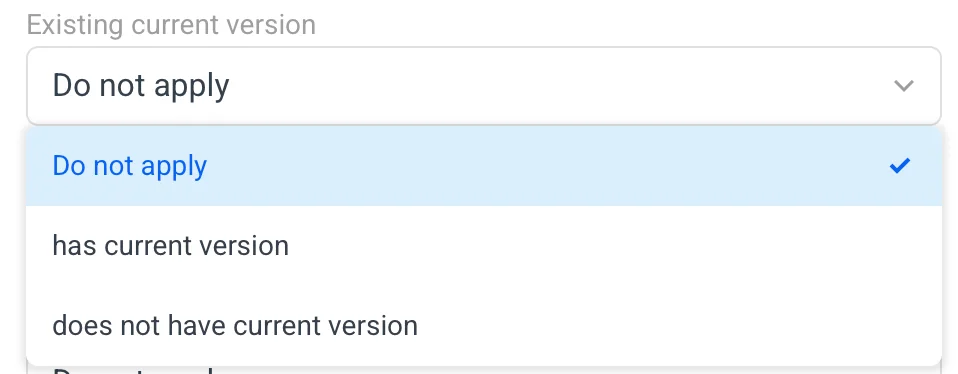
The filter compares the current state of the translation to a list of selected choices out of this list:
Existing current version:
- Do not apply
- has current version
- does not have current version
Awaiting review:
- Do not apply
- is waiting for review
- is not waiting for review
Source changed state:
- Do not apply
- has the source changed state set
- does not have the source state set
Need improvement flag:
- Do not apply
- has the need improvement flag set
- does not have the need improvement flag set
State filters allow you to fine-tune the behavior to only apply the automation to an untranslated key in the given language, etc.
🔖 Filter by Tags 🔗
This filtering is available for all actions. The rule is only invoked if the key, translation, or version (depending on what is available based on the trigger event) carries at least one of the included tags and none of the excluded tags. Translation tags are used for prioritizing translations and organizing content.
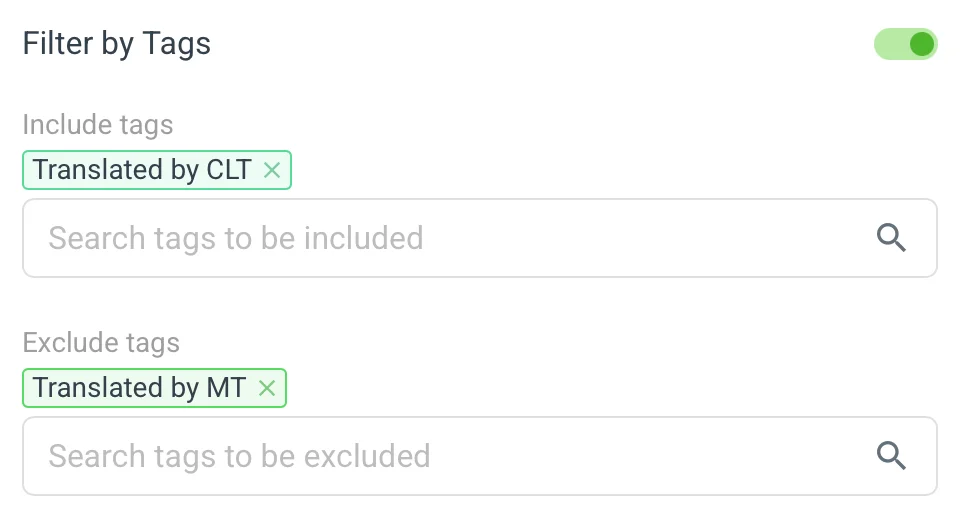
Most likely, you will want to use filtering with automatically assigned tags, which are:
Translated by MT | Automatically added to translations provided by MT engines integrated with Localazy. |
Translated by CLT | Automatically added to translations provided by our professional translators. |
Reviewed by CLT | Automatically added to translations reviewed by our professional translators. |
✏️ Filter Content 🔗
It allows you to define a list of inclusive and exclusive rules that compare key, source text, translations, context comments, or file paths to the configured value.
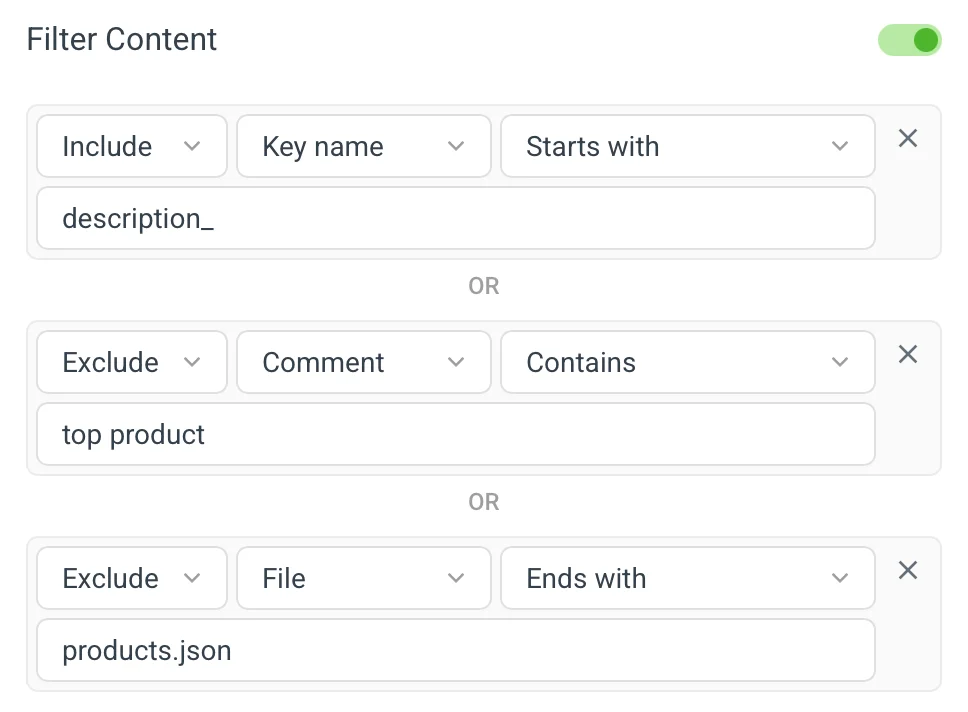
This filtering is available for all actions, but the options may differ. For example, it's not possible to compare a translation for Use machine translations as it's only triggered for the source language.
Available rules:
Missing/Empty | The input is missing or empty. |
Exact match / Exact match (case insensitive) | The input exactly matches the value. |
Contains / Contains (case insensitive) | The input contains the value. |
Starts with / Starts with (case insensitive) | The input starts with the value. |
Ends with / Ends with (case insensitive) | The input ends with the value. |
Regex expression | The input matches the provided regex expression. |
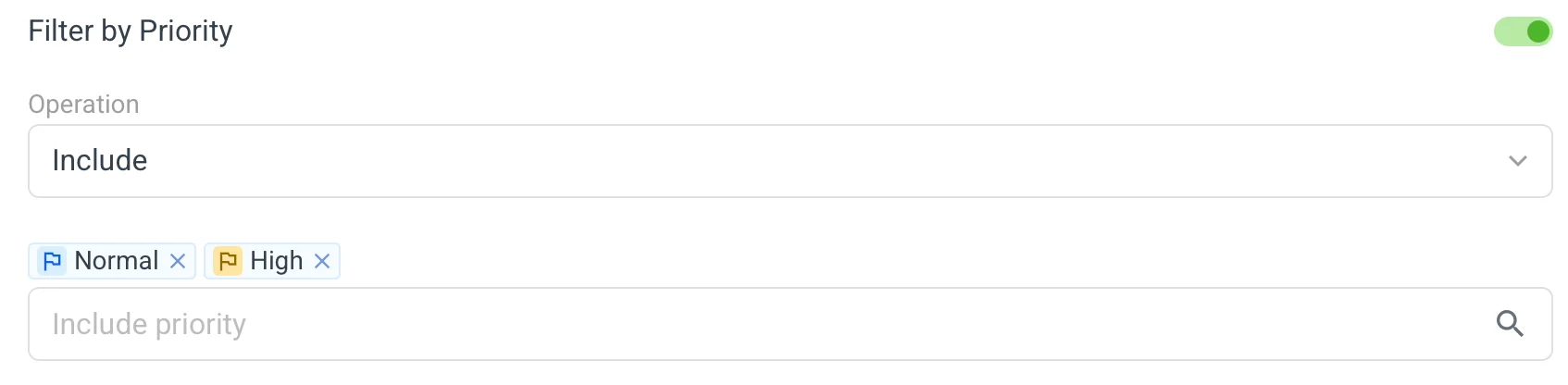
🔴 Filter by Priority 🔗
Select which source key priorities to include or exclude from the automation. This filter is commonly used with the Use machine translations action to automatically translate source keys with (usually) low or lowest priority, allowing you to focus human translation efforts on high-priority content.
Source & translation - plurals and lists
The normal single key is encoded as is. For filters to work easily with more complex values, plurals and string lists are encoded this way:
Plural
ONE: one form
OTHER: other formList
- item 1
- item 2
- item 3✅ Conclusion 🔗
In summary, Automations enriched with filters offer a tailored approach to translation management, allowing you to optimize the efficiency and precision of the actions. You can customize actions based on specific criteria such as language, user roles, and tags.
Want to test how good these filters are in practice? Find the Automations feature on your Localazy Dashboard under Tools, and try it out.




